Brief Introduction:
Blockchain technology is quickly becoming one of the 21st century’s most significant innovations. Industries all around the world are changing as a result of its decentralized structure and enormous possibilities. However, what is blockchain and why is it regarded as the cornerstone of technology in the future? We will go further into blockchain technology in this extensive guide, examining its workings, uses, advantages, difficulties, and potential.
What is Blockchain
Blockchain is fundamentally a decentralized digital ledger that keeps track of transactions on several computers. Blockchain functions on a peer-to-peer network, guaranteeing security and transparency in contrast to conventional databases run by a central authority.
Key Components of Blockchain
- Blocks: Every block has a distinct hash value (similar to a fingerprint), data, and a timestamp.
- Chains: A chain is made up of blocks connected in chronological sequence.
- Decentralized Network: Since the data is spread across several nodes (computers) rather than being kept in one place, it is practically hard to change.
In contrast to conventional databases, blockchain ensures that data is unchangeable once it is recorded, removes middlemen, and lowers the possibility of fraud.
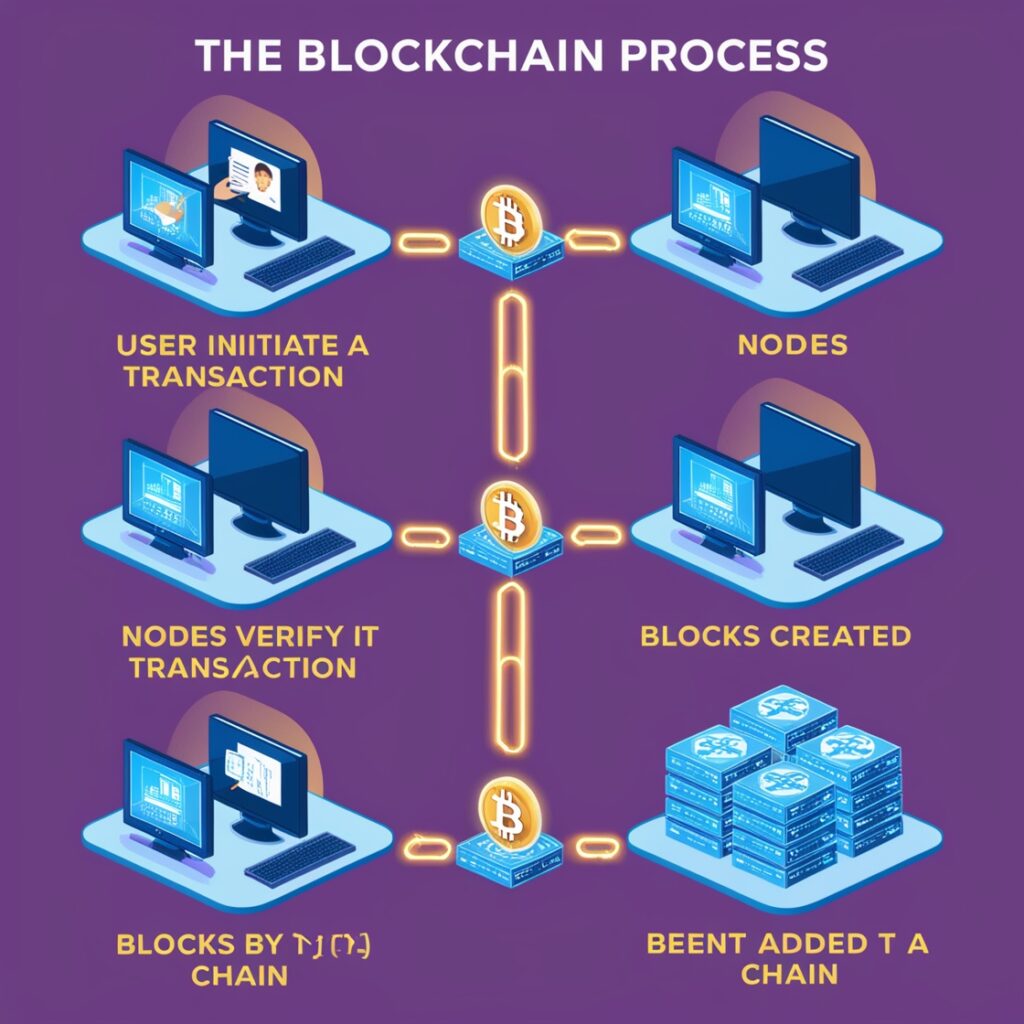
How Blockchain Works:
To understand how blockchain operates, it’s essential to break down its process:
Step 1: Initiating a Transaction
A user makes a request for a transaction, like a smart contract creation or cryptocurrency transfer.
Step 2: Verification by Nodes
The network of nodes is broadcast the transaction. Every node uses cryptographic techniques to confirm the transaction.
Step 3: Adding to the Block
The transaction is joined with other transactions to create a block when it has been validated.
Step 4: Consensus Mechanism
Nodes use techniques such as these to agree on the block’s validity:
- Proof of Work (PoW): To verify the block, nodes must solve challenging mathematical puzzles.
- Validators are selected according to the quantity of coins they possess and are prepared to “stake.” This is known as Proof of Stake (PoS).
Step 5: Linking the Block
Secured by cryptography, the validated block is appended to the current blockchain.
Step 6: Completion
Every node updates its copy of the blockchain after the transaction is finished.
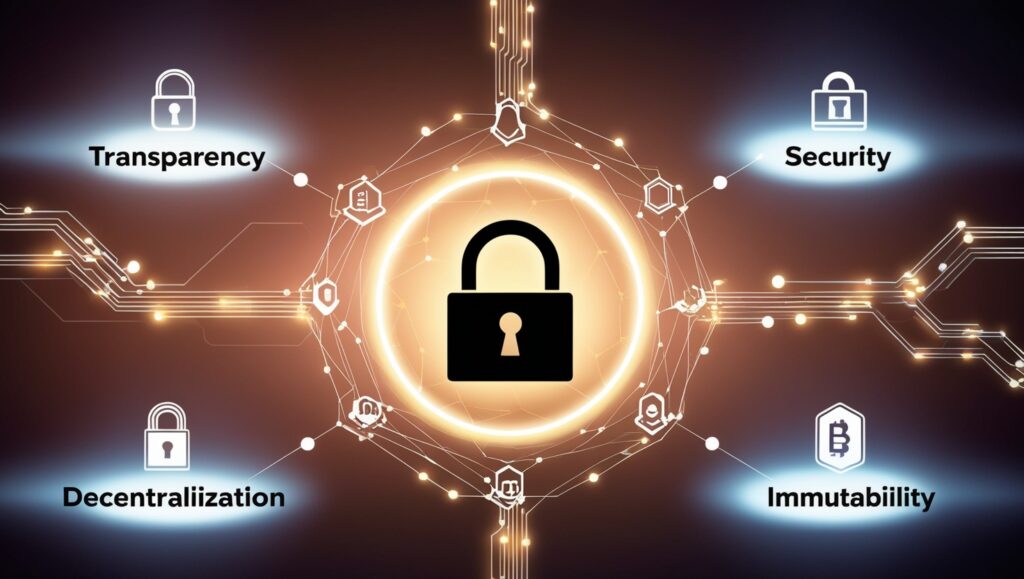

Characteristics of Blockchain
P2P Network differs from other technologies due to its distinct features:
Decentralization
P2P Network divides power across several players, improving security and dependability in contrast to centralized systems where data is controlled by a single entity.
Transparency
All parties may see every transaction on a P2P Network , which promotes accountability and trust.
Immutability
Data integrity is guaranteed since once information is entered to a P2P Network , it cannot be removed or changed.
Security
P2P Network employs cutting-edge cryptography methods to shield data from manipulation and unwanted access.
Real-World Applications of P2P Network
P2P Network technology is not limited to digital currencies such as Bitcoin. It is changing industries all around the world:
Finance:
P2P Network makes cross-border payments safe, quick, and affordable. Additionally, it powers decentralized finance (DeFi) services and cryptocurrencies.
Supply Chain Management:
Blockchain makes supply chains more transparent and traceable. It can, for instance, trace a product’s path from producer to customer, guaranteeing its legitimacy.
Healthcare:
Blockchain-stored patient records are safe, impenetrable, and only accessible by authorized individuals, all of which enhance patient care.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that do not require middlemen because their conditions are encoded directly into the code.
Voting Systems:
Voting systems based on blockchain improve election security and transparency while lowering the possibility of fraud.
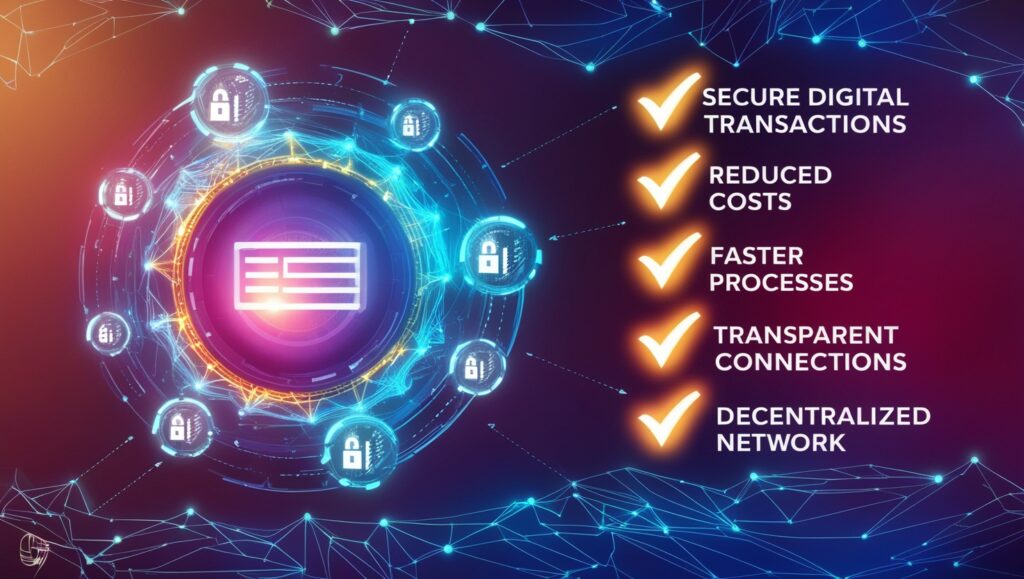
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain has many advantages:
Enhanced Security:
It is extremely safe because to its decentralized and cryptographic design, which lowers the possibility of fraud and hacking.
Cost Efficiency:
P2P Network drastically reduces transaction costs by doing away with middlemen.
Speed
Transactions are handled far more quickly than with conventional techniques, especially when making cross-border payments.
Transparency and Trust
By guaranteeing that every transaction is transparent and verifiable, blockchain promotes confidence among users.
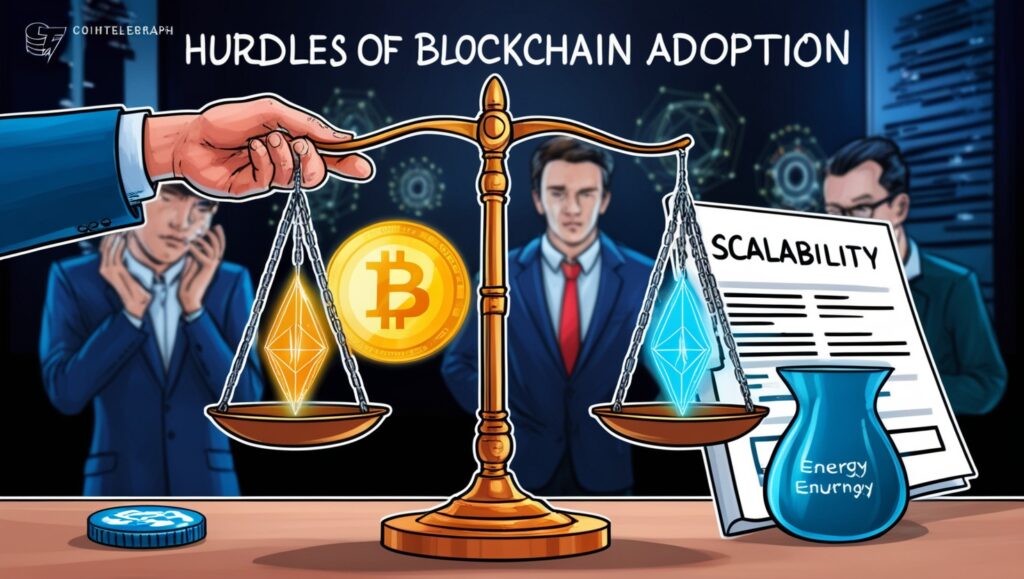
Challenges in Blockchain Adoption
Despite its potential, P2P Network faces several hurdles:
Scalability
Delays result from most blockchains’ inability to manage many transactions at once.
Energy Consumption:
PoW and other consensus techniques use a lot of energy, which is problematic for the environment.
Regulatory Issues:
The regulation of P2P Network technology and its applications continues to be a challenge for governments worldwide.
Lack of Awareness:
Blockchain adoption is limited because many individuals and organizations lack a thorough understanding of it.
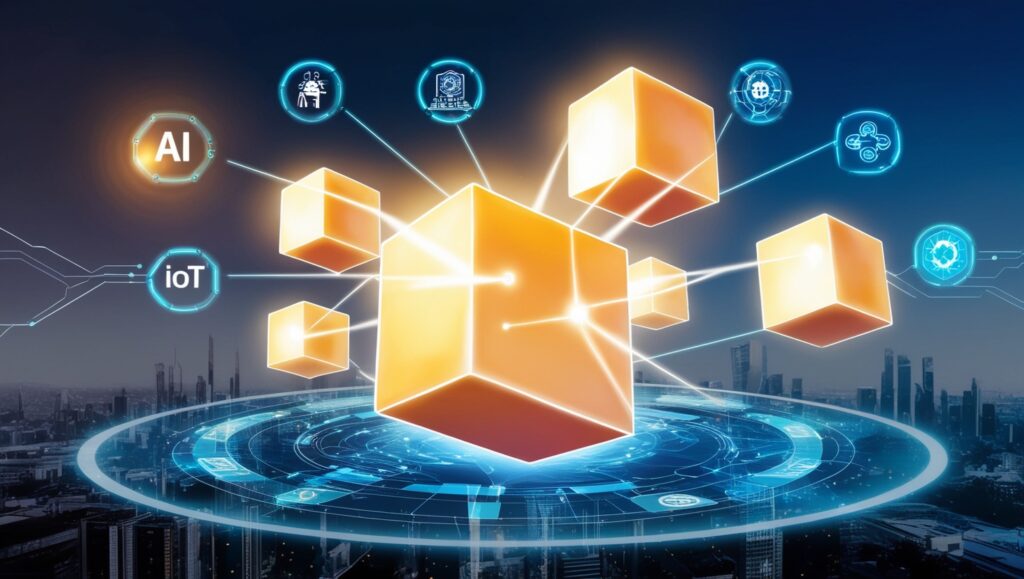

The Future of Blockchain
P2P Network is poised to play a pivotal role in the future of technology.
Improved Scalability and Sustainability:
Current constraints are being addressed by emerging solutions like sharding and energy-efficient consensus techniques.
Integration with Emerging Technologies:
P2P Network is opening up new opportunities by integrating with Web3, the Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence (AI).
Transformation Across Industries:
Blockchain will continue to upend established systems in industries like healthcare and banking, resulting in more transparent and effective procedures.
Conclusion:
Blockchain is a mindset shift rather than merely a technology. It serves as a basis for upcoming developments due to its capacity to offer decentralization, transparency, and security. Even though there are still obstacles to overcome, the continuous developments in blockchain technology portend a more secure, efficient, and just future for industries.
The time to investigate blockchain and its ability to change the world has come, regardless of whether you are a computer enthusiast, corporate leader, or an inquisitive student.
